What is De Quervain Syndrome?
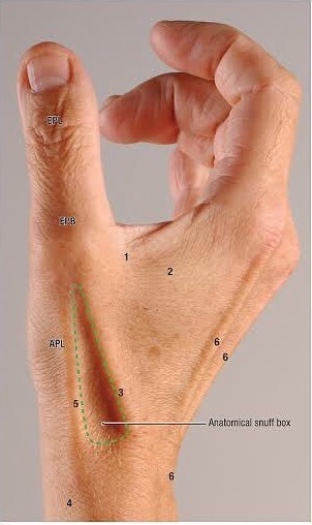
Inflammation of the two tendons and their sheaths that control the movement of the thumb.APL, EPB
*syndrome What it means: It is a group or group of symptoms that occur at the same time.
*tendon: Rope-like structures that connect muscles to bones so that the muscles can pull on the bones and move them.
anatomy:
The thumb has 2 major tendons that help pull the thumb away from the index finger and help straighten the thumb joint.
The 2 main tendons are:
- abductor hallucis longus. APL“Aids thumb abduction”
- Extensor hallucis brevis. Environmental Protection Agency. “Helps Thumb Stretch”
- Environmental Protection Agency:
origin: ½ dorsal side of the radius.
insert: The proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Function: Thumb extension.
Inside: interosseous ramus of radius
- Application language:
origin: Dorsal side of radius and ulna.
insert: Base of metacarpal bone.
Function: thumb abduction
Innervation: Same as EPB.
*These two tendons originate in the muscles of the forearm and then run together in a sheath close to the bone, crossing from the thumb side of the wrist into the hand.
Any swelling or irritation of these two tendons and the thickness of the sheath can cause inflammation and the tendons no longer fit into the sheath.
Clinical points:
- Inflammation of the tendon at the base of the thumb.
- Causes pain, tenderness, and swelling on the affected side.
- Common in 30-50 years old, “more women than men”
- Diagnosed by Finkelstein test.
The main causes of De Quervain syndrome:
- Excessive use of the thumb and wrist.
- Associated with pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Can be caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
- Repeatedly grasping, lifting and grasping objects.
- Play golf, play the piano, and more.
- Occupational and work-related risk factors: office workers and prolonged computer use.
Signs and symptoms of De Quervain syndrome:
- The main symptoms: pain On the radially “outer side” of the wrist.
- Pain may come on gradually or suddenly. “
- From the wrist, it can be called the forearm.
- The pain usually gets worse when the hand and thumb are overused.
- Pain, burning pain.
- swelling on the thumb side. This swelling may be a fluid-filled cyst in the wrist area.
- capture or capture Feel when moving the thumb.
- wrist limitation ROM.
- Weakness of the forearm and wrist muscles.
- local swelling and tenderness In the area of the radial styloid.
Differential diagnosis:
- Trigger thumb.
- Superficial radial nerve neuritis. “Wattenberg Syndrome”
- Arthritis of the first MCP joint is the main differential diagnosis of DQ.
- Scaphoid fracture.
- Radial styloid fracture.
Physical examination for De Quervain syndrome:
Check the thumb side of the hand for any pain or swelling.
test..
Finkelstein test:
- Patient position: sitting or standing.
- The patient’s hand is relaxed and comfortable.
- The therapist asks Px to make a fist, fingers wrapped around the thumb.
- Therapist stabilizes forearm and adducts wrist “Ulnar deviation” >> Tightens APL, EPB tendons.
- test positive: Pain on one side of the wrist. “Reproduction of Px symptoms”
negative test: Px Not feeling any pain radiating to the side of the thumb.
Management of De Quervain Syndrome:
- rest.
- ice.
- splint.
- NSAIDs.
- Activity modification.
- Surgery: applied only when conservative management fails,
the primary goal of the surgery; Open the dorsal compartment of the sheath to free the irritated tendon.
The opening relieves stress on the tendon and restores free tendon glide.
Physiotherapy Management:
exist acute phaseice can reduce tendon sheath inflammation.
Heat may help relax and loosen tight muscles.
- rest: Secure thumb and wrist.
- Thumb Splint: Keep the thumb and wrist straight with a splint or brace to rest the tendons.
- Ultrasound therapy.
- athlete:”MWM” to reduce pain and improve ROM of the wrist.

- Activity modification: Avoid repetitive thumb movements.
- take more exercise: It should be carried out gradually after the pain is under control, such as:
- isometric front.
- weird ex.
- Concentric front.
- Radial nerve sliding.
You can watch the video on top 5 strengthening ex for more understanding.
- Sticking therapy: Can help relieve pain and improve wrist function and support.
- massage: Deep tissue massage to relieve pain and tightness of thenar muscles.
in conclusion:
DQ tenosynovitis syndrome is a painful disorder that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. If you have this syndrome, you feel soreness or burning pain when you turn your wrist, grasp objects, or make a fist.
Recent research reviews on DQ syndrome:
Mom’s Thumb: De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis in New Moms with Cardiomyopathy
Literature review of DE-QUERVAINS tenosynovitis
refer to:
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. (2022). Orthoinfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/de-quervains-tendinosis/
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. (ND). physiology. https://www.physio-pedia.com/De_Quervain%27s_Tenosynovitis
- De Quervain tendonitis. (ND). slideshow player. https://www.google.com/amp/s/slideplayer.com/amp/14766730/
- Yew Tree (2013). De Quevin’s. Slide sharing. https://www.slideshare.net/chongyewlee/de-quervains
- Finkelstein test. (2022). Phsiopedia. Retrieved from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Finkelstein_Test