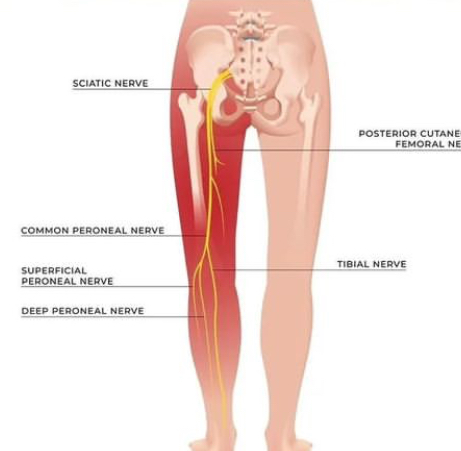
sciatic nerve anatomy
sciatica The nerve is the largest in the body, and it consists of several spinal nerves that cover and run from the waist to the knees. “from L4_S3”
It travels from the lumbosacral plexus in the lower back and sacrum, through the greater sciatic foramen, into the buttock region, the back of the thigh, splits into the tibial and common peroneal nerves, enters the calf, anterior and lateral compartments of the leg, and enters the foot.
branches sciatic nerve
- Articular branch: arises proximally and supplies the hip joint via the posterior capsule.
- Muscular Branches: The ischial portion that supplies the hamstrings and adductor magnus.
- The distal terminal branches are the tibial and common peroneal nerves.
sciatic nerve dermatome:”sensory innervation”
It is an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve. From (L4-S3).
- L4 >> Bend forward from the outside of the thigh to the inside of the calf and foot.Includes knee, inner big toe, and medial malleolus
- L5 >> Wrap the rear outer side of the thigh in front of the level of the knee to cover the front outer side of the leg.
- S1 >> Extends the posterolateral aspect of the thigh, popliteal area, and calf to the lateral malleolus, then to the lateral edge of the foot, heel, and pinky toe
- S2 >> Extends from the buttocks to the inner thigh, popliteal and calf.
- S3 >> Posterior includes inner buttocks and perineal area.
Motor pathway of the sciatic nerve. “According to the nerve root”
- S1: Ankle plantarflexion and eversion/knee flexion
Definition sciatica
Sciatica is pain, numbness, or tingling in the back of the leg that originates in the back and spreads to the buttocks, buttocks, and legs.
Why is it called sciatica?
due to problems or compression sciatica nerve.
Clinical considerations:
- Women outnumber men.
- Often occurs after the age of 40.
- Rarely occurs before age 20.
- It’s not a disease, it’s a symptom.
Causes of sciatica:
Herniated disc:
CD Acts as a cushion between the vertebrae. As we age, these discs weaken and become more prone to injury.
The gelatinous center of the disc sometimes pushes through the outer layer and compresses the sciatic nerve root.
The worn and torn nature of the vertebrae can lead to narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing, called spinal stenosis, can put pressure on the sciatic nerve root.
- Spondylolisthesis:
This is a slip of one vertebra so that it is out of alignment with the vertebra above, narrowing the opening for the nerve to exit. As a result, the stretched spine may pinch the sciatic nerve.
- Spinal Tumors:
In rare cases, sciatica may be caused by a tumor growing inside or along the spinal cord or sciatic nerve. As the tumor grows, it increases pressure on the nerves that branch off from the spinal cord.
- inflammation.
- Infect.
- injury, such as a broken bone.
- Piriformis Syndrome:
The piriformis is a muscle located deep in the buttocks. It connects between the lower spine and the upper thigh bone, and directly over the sciatic nerve.
- If this muscle spasms, it can compress the sciatic nerve and cause sciatica symptoms.
- Piriformis syndrome is more common in women.
This condition affects men who keep their wallets in the back pocket of their trousers. This causes chronic compression of the piriformis muscle and can stress the sciatic nerve over time.
hint: You can avoid this problem by keeping your wallet in your front pocket or jacket pocket.
risk factors
- age:
Age-related changes in the spine, such as herniated discs, are the most common cause of sciatica.
- obesity:
Extra body weight can cause changes in the spine that cause sciatica due to increased pressure on the spine.
- Profession:
Jobs that involve twisting your back, lifting heavy objects, or driving a motor vehicle for long periods of time can cause sciatica.
- sedentary.
People who sit for long periods of time or are sedentary are more likely to develop sciatica than those who are active.
5. Diabetes.
This condition can affect how the body uses blood sugar, increasing the risk of nerve damage.
6. Pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms:
How do I know it’s sciatica?
- pain:
Persistent burning, tingling, or tingling that starts in the lower back or buttocks and radiates down the thighs, calves, and front or back of the feet.
- numbness: on the back of the leg.
- Unilateral symptoms:
Sciatica usually affects one leg. “The patient feels a heaviness in the affected leg”.
**rareBoth legs may be affected together.
- Posture-induced symptoms:
Symptoms of sciatica may feel worse when sitting, trying to stand, bending the spine forward, twisting the spine, lying down, and coughing.
- Symptoms are relieved by walking.
investigation
1. X-rays.
2. NMR.
3. CT scan.
4. Electromyography: Measures the speed at which nerve signals travel through the body.
special test
Treatment and Management:
How long does sciatica usually last?
Most people with sciatica (90%) get better spontaneously over time, days or weeks with self-care treatment.
What are the two treatments for sciatica?
surgical
Unresponsive to physical therapy management in severe cases.
- Laminectomy: Have spinal stenosis.
- Microdiscectomy: Have lumbar disc herniation.
Physiotherapy
- In the acute phase (pain management).
- ten.
- ice.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: such as naproxen ibuprofen
- Positioning exercises (flexion or extension position).
- Strengthens and stretches.
- Piriformis foam roller.
- Supine piriformis stretch.
- Glide the sciatic nerve in the supine position.
- Lie on your stomach and press upwards.
- acupuncture.
- massage.
- hot pack.
- Manipulation and mobilization.
- Stretch the piriformis muscle.
- Gait training.
- Muscle Energy Techniques
- Mackenzie method.
 in conclusion
in conclusion
Sciatica is caused by injury, irritation, inflammation, pinching, or even compression of the sciatic nerve in the lower back. The most common cause is a herniated or slipped disc, which puts pressure on the nerve roots.
refer to
- Mayo Clinic staff. (September 13, 2022). sciatica. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved February 15, 2023 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sciatica/symptoms-causes/syc-20377435
- Prudden, G. (n.d.). sciatic nerve. Physiology. Retrieved February 15, 2023 from https://www.physio-pedia.com/Sciatic_Nerve
- Mayo Clinic staff. (September 13, 2022). sciatica. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved February 15, 2023 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sciatica/symptoms-causes/syc-20377435
- Cleveland Clinic Medical Specialist. (March 25, 2020). Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention and Pain Relief. Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved February 15, 2023 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12792-sciatica
- Stephen Hochschuler, MDP-RBDH (2023). What You Need to Know About Sciatica. Spine health. . Retrieved February 15, 2023 from https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/sciatica/what-you-need-know-about-sciatica